PICWaveA photonic IC, laser diode and SOA simulator |
    |
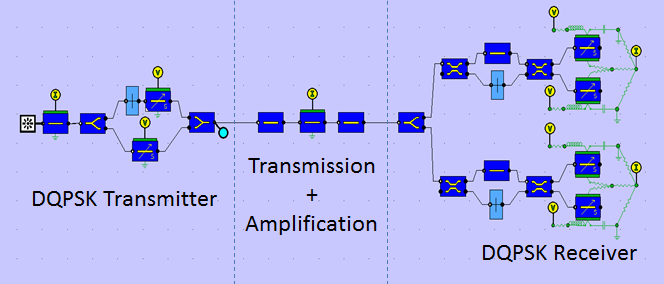
Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (DQPSK)Simulation with PICWave softwareThis example demonstrates differential quadrature phase shift keying (DQPSK) modulation and demodulation, illustrating a powerful combination of PICWave's capabilities including: phase-modulation, SOA amplification, noise, electrical circuit elements and oscilloscope analysis/constellation diagrams. In the circuit (shown below), a DQPSK phase-encoded signal is generated by a DQPSK transmitter. This then passed through an attenuating waveguide to emulate optical fibre loss, and is then amplified by an SOA. The amplified signal is then passed to the DQPSK receiver which recovers an intensity-encoded signal from the phase-encoded signal.
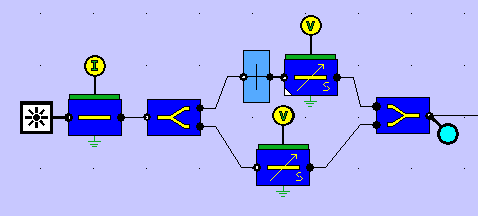
The DQPSK transmitter consists of a CW optical signal injected into an MZI modulator. The MZI has a constant π/2 phase shift between its two arms, and on each arm of which a [0,π] phase modulation is applied using voltage signals corresponding to the in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components of the DQPSK signal.
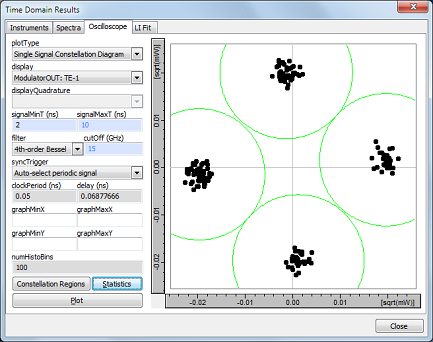
A 40Gb/s DQPSK-encoded signal emerges from the transmitter with the following constellation diagram.
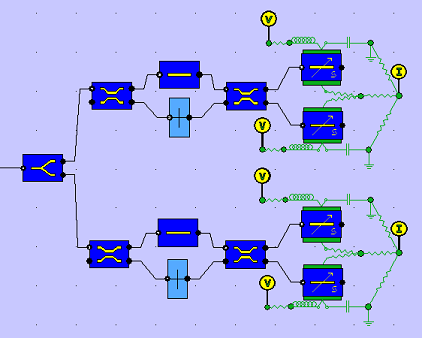
The receiver begins with two MZIs whose path differences select the in-phase(I) and quadrature (Q) components of the DQPSK signal, respectively. These MZIs convert the differential phase signals into intensity signals. The MZIs are followed by balanced photo-detectors which generate the I and Q bit sequences as electrical signals.
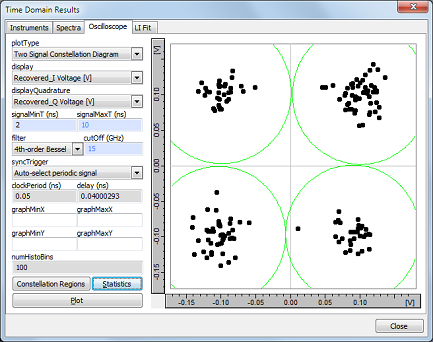
The constellation diagram of the received signal is shown below. The increased noise and BER of 10-6 arise from the spontaneous emmision noise in the SOAs and shot noise at the electrical contacts of the photodiodes.
|